VMware Cloud on AWS includes resiliency at different layers. We are all familiar with vSphere HA protecting against ESXi host failures. With VMware Cloud on AWS, ESXi hosts reside in an AWS availability zone and are protected by vSphere HA. What about protection for the availability zone the ESXi hosts reside in? While an AWS availability zone failure is a rare occurrence, customers should know they also are protected at this layer as well. A new feature called Stretched Clusters for VMware Cloud on AWS is designed to protect against an AWS availability zone failure. Now applications can span multiple AWS availability zones within a VMware Cloud on AWS cluster. If an application instance fails the second instance in another availability zone can take over. This, of course, depends on if the application includes this level of availability. Let’s take a look at the Stretched Clusters feature.
Infrastructure Configuration
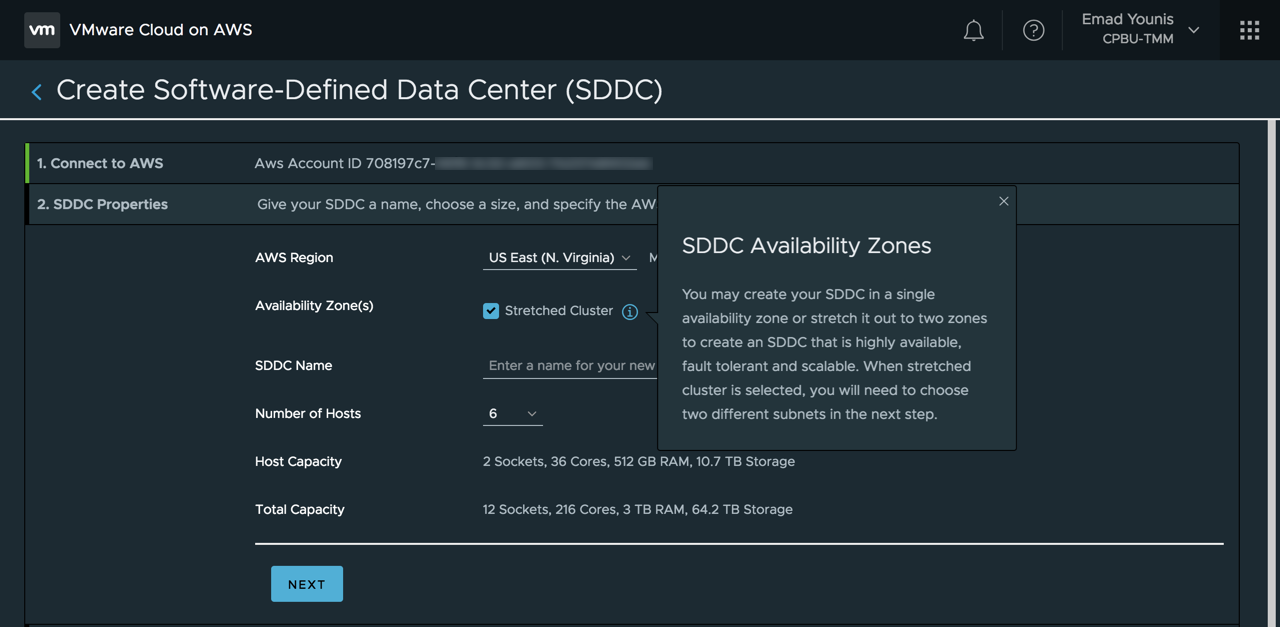
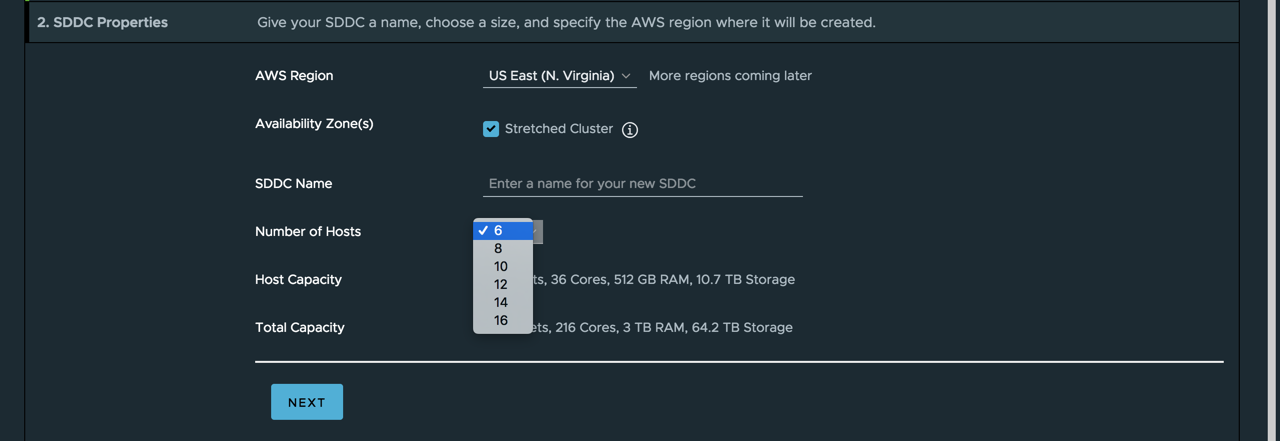
The Stretched Clusters feature deploys a single SDDC across two AWS availability zones. This option is only available during the SDDC creation steps under SDDC properties. When enabled the default number of ESXi hosts supported in a Stretched Cluster is six. Additional hosts can be added later but must to be done in pairs across AWS availability zones.
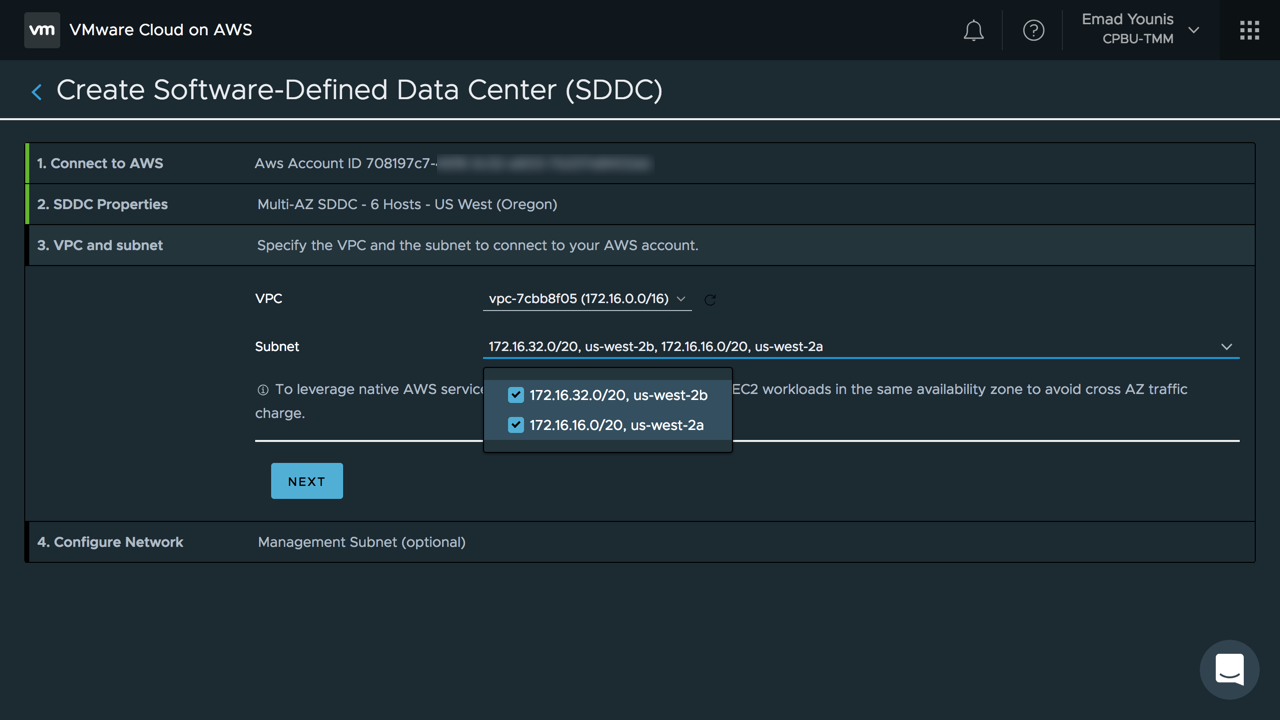
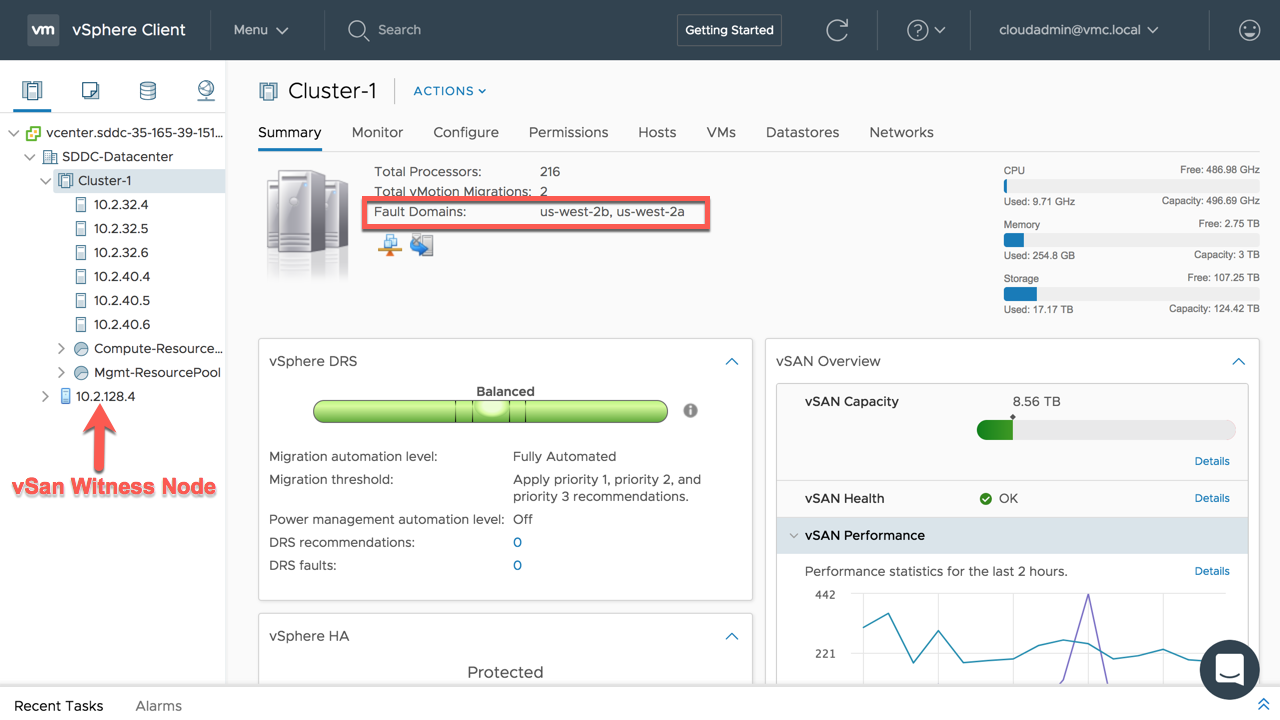
The Stretched Clusters feature requires an AWS VPC with two subnets, one subnet per availability zone. The subnets determine an ESXi host placement between the two availability zones. As an SDDC is deploying, it provisions three hosts in each AWS availability zone and creates a vSAN stretch cluster across the two availability zones. The vSAN stretched cluster allows synchronous writes across the two availability zones. A vSAN witness node appliance, which looks like an ESXi host, will automatically be provisioned. It resides outside the SDDC cluster and in a third AWS availability zone. The vSAN witness node appliance is required in case network communication is lost, assisting to avoid split brain for virtual machines across AWS availability zones. Logical networks are also extended using NSX to support workload mobility across the two AWS availability zones.
Workload Management
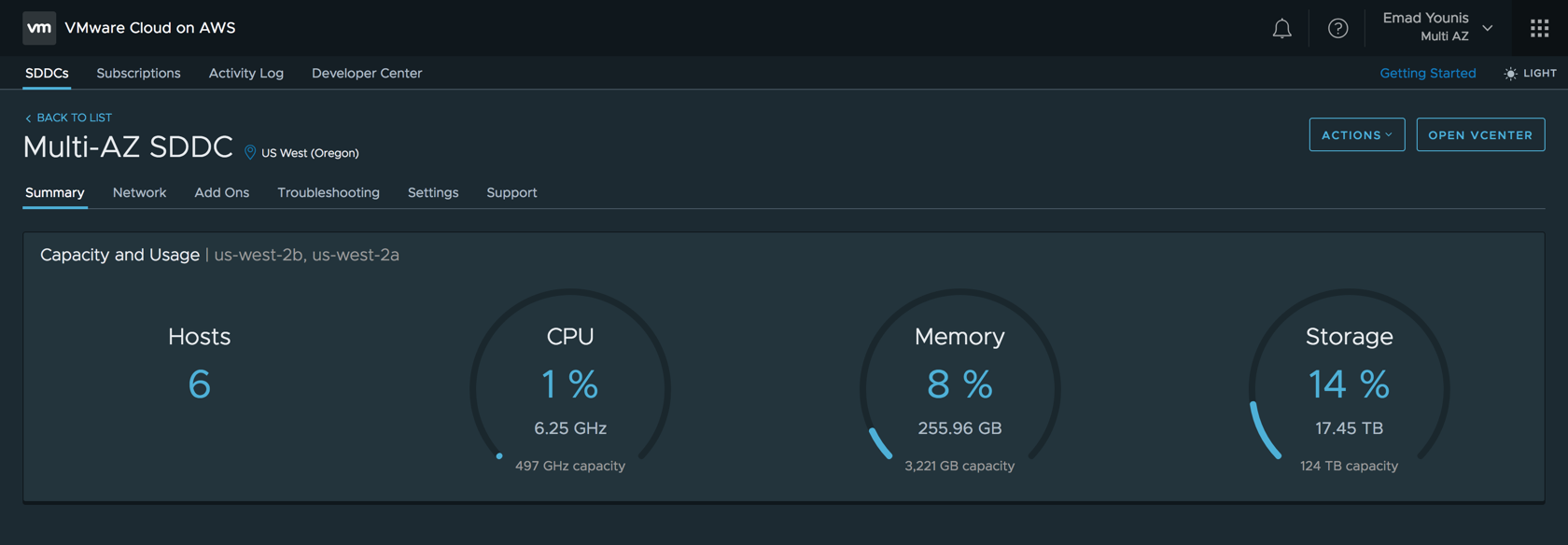
Once a stretched clusters SDDC is available, go to the summary tab and view the VMware Cloud on AWS console. The console displays the capacity and usage of the SDDC for the two AWS availability zones.
Now let’s login to vCenter Server. Here the SDDC will appear as a single logic datacenter with two fault domains. The ESXi hosts in the cluster span the two AWS availability zones. Customers can view which availability zone each host resides in from its summary tab. The fault domains listed correlate to the given AWS availability zone name. For a single view of all the ESXi hosts in a cluster and their fault domain, select the cluster and go to the Hosts tab. Within the Hosts tab, add the fault domain column.
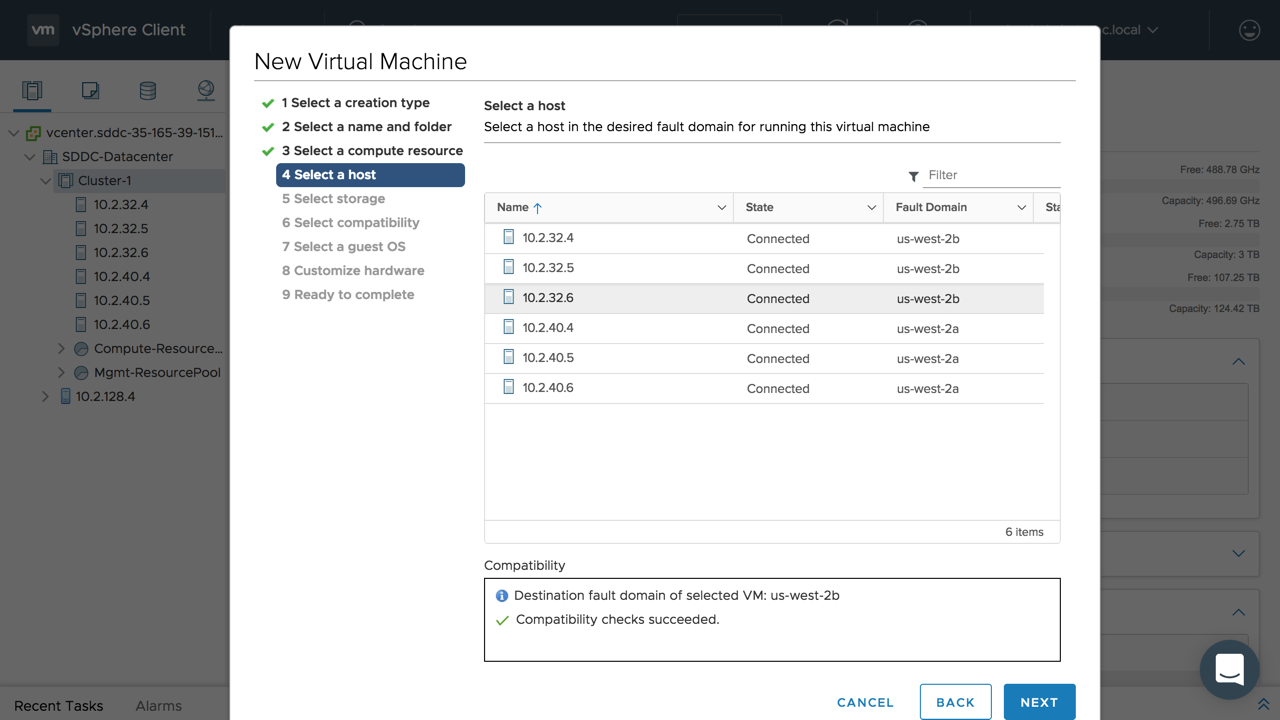
When provisioning virtual machines, customers have options when deploying to an availability zone. The first option is auto placement. This occurs at the cluster level, where DRS will handle the placement of the workload. A more granular option is selecting a host in an availability zone to deploy virtual machines to. DRS will honor the virtual machine availability zone placement as a sticky rule. It will only move the virtual machine in case of a failure. vSphere HA will attempt to honor this placement decision if possible. An availability zone failure will have the same behavior as a vSphere HA event. All virtual machines in the failed availability zone will get restarted in another availability zone. vSphere HA restart priority is also taken into account:
- vCenter Server has the highest restart priority. Other management virtual machines have a high restart priority
- Virtual machines migrated (cold or live) from on-premises will keep their restart priority
- New Virtual Machines created on a stretched cluster will restart after other higher priority virtual machines
Customers now have full resiliency for their mission-critical applications across AWS availability zones with zero RPO due to synchronous replication built in natively in their Cloud SDDC. You can use the VMware Hands-On Labs to test drive VMware Cloud on AWS and this new product walkthrough and video to get familiar with the Stretched Clusters feature. Glenn Sizemore will also have a blog post coming with more details on the how storage works with Stretched Clusters, stay tuned.